Embarking on a startup adventure can be a thrilling yet daunting endeavor. As a budding entrepreneur, you’ll inevitably encounter two buzzworthy terms – MVP (minimum viable product) and MMP (minimal marketable product). While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct approaches to product development and launch. Is startup MVP development better? Or is it MMP?
In this article, we’ll explore the key disparities between MVP development and MMP development, weigh their pros and cons, delve into their applications, and shed light on the effective combination of these strategies. So, let’s jump right in!
Understanding MVP and MMP
MVP and MMP are strategic tools employed by startups to test ideas and gain invaluable insights before diving into full-scale product development. Although they share commonalities, it’s crucial to grasp their nuances.
The MVP Development Approach
MVP, as the moniker implies, focuses on creating the bare essentials needed for a product to be deemed viable. Its aim is to validate assumptions, gather user feedback, and iterate based on that feedback. The primary advantages of MVP development include:
Swift Time-to-Market: By swiftly developing a rudimentary version of the product, entrepreneurs can launch faster and commence gathering user data from the get-go.
Cost-Efficiency: MVP development allows startups to minimize expenses by sidestepping the extensive development of features that may not resonate with the target audience.
Iterative Refinement: The feedback collected from early adopters facilitates continuous improvement, ensuring the product aligns with customer needs.
However, MVP development also carries limitations:
Potential User Dissatisfaction: Introducing a product with limited functionality may leave users dissatisfied if their core requirements aren’t adequately addressed.
Extended Development Cycles: The iterative nature of MVP development can prolong the development process, necessitating multiple iterations to achieve a satisfactory product-market fit.
The MMP Development Approach
In contrast, MMP focuses on developing a product with the bare minimum features required to captivate a viable market segment. Its objective is to deliver value to customers while simultaneously gauging the market’s response. The primary advantages of MMP include:
Customer Satisfaction: By zeroing in on a specific market segment and catering to their needs, MMP ensures a higher level of customer contentment.
Early Revenue Generation: With a marketable product in hand, entrepreneurs have the opportunity to generate revenue while refining and expanding their offering.
Competitive Edge: Being the trailblazer in offering a solution tailored to a specific market niche can bestow a significant competitive advantage.
Nonetheless, MMP comes with certain considerations:
Limited Market Reach: Concentrating on a particular market segment may inadvertently lead to missing out on potential customers beyond that segment’s confines.
Higher Development Costs: Crafting a marketable product requires additional features and functionality, thereby driving up development costs.
Combining MVP and MMP
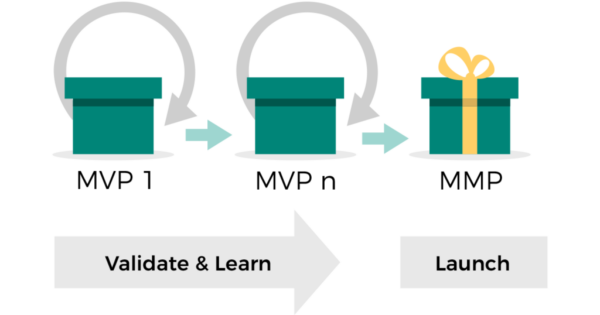
While MVP and MMP may initially seem like opposing strategies, they can be effectively amalgamated to maximize benefits and mitigate drawbacks. The key lies in leveraging the strengths of each approach at different stages of the startup journey. Here’s a suggested roadmap:
Begin with MVP: Commence by building a rudimentary version of the product that tackles the core pain points of the target audience. Launch it to a select group of early adopters and gather their invaluable feedback.
Iterate and Enhance: Utilize the feedback received to make iterative improvements, gradually enhancing the product’s functionality and addressing user needs.
Transition towards MMP: Once the product attains a satisfactory level of viability and validation, shift gears to develop additional features catering to a specific market segment.
Market Testing: Launch the MMP to the identified market segment while actively collecting feedback and refining the offering based on user responses.
Expand and Scale: As the product gains traction within the target market, contemplate expanding to new market segments while upholding the core value proposition.
Launching a Successful Startup – Where to Begin?
Starting a successful startup requires careful planning and strategic execution. Here are some essential steps to guide you on your journey:
Identify a Problem
- Thoroughly research the market to identify a pressing problem or pain point that your product or service can effectively address.
- Analyze existing solutions and determine how your idea can offer a unique and compelling value proposition.
- Consider conducting surveys or interviews with potential customers to gain deeper insights into their needs and challenges.
Validate the Idea
- Conduct market research to validate the demand for your solution and determine the size of your target market.
- Study your competitors and identify gaps or opportunities where your product can stand out.
- Use tools like surveys, focus groups, or landing page tests to gauge interest and collect feedback on your idea.
Build a Strong Team
- Assemble a talented and diverse team that complements your skillset and shares your entrepreneurial vision.
- Look for individuals with expertise in areas such as product development, marketing, finance, and operations.
- Seek team members who are passionate, motivated, and capable of working collaboratively in a fast-paced startup environment.
Develop a Robust Business Plan
- Create a comprehensive business plan that outlines your goals, target market, competitive analysis, and financial projections.
- Clearly define your unique selling proposition and map out your marketing and sales strategies.
- Include a detailed budget, revenue streams, and a timeline for milestones and growth.
Build the Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Start developing your MVP, focusing on the core features that address the identified problem and provide value to your target audience.
- Prioritize functionality over aesthetics and avoid unnecessary features that can delay the product launch.
- Consider using agile development methodologies to quickly iterate and make improvements based on user feedback.
Launch and Gather Feedback
- Release your MVP to a select group of early adopters or beta testers who fit your target market profile.
- Collect feedback through surveys, interviews, or analytics tools to understand user experiences and pain points.
- Use the insights gathered to refine and enhance your product, iterating on features and addressing user needs.
Scale and Expand
- Once you have achieved product-market fit and received positive feedback, focus on scaling your operations and expanding your customer base.
- Develop a robust marketing and customer acquisition strategy to reach a broader audience.
- Explore partnerships, strategic alliances, or distribution channels that can help accelerate your growth.
Continuously Innovate
- Keep a pulse on the market, industry trends, and customer preferences to stay ahead of the competition.
- Stay open to feedback, pivot if necessary, and adapt your product or strategy based on market demands.
- Foster a culture of innovation within your team, encouraging creativity and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
In the journey of building a successful startup, the choice between MVP and MMP plays a pivotal role. While MVP development concentrates on constructing a viable product with minimal features, MMP focuses on capturing a specific market segment with a minimal feature set. By synergistically blending the strengths of both approaches, startups can chart their course towards a successful product launch. Remember, it’s essential to comprehend your target audience, validate your ideas, and continually iterate based on user feedback. So, embark on your entrepreneurial adventure armed with the knowledge of MVP and MMP, and pave the way for your startup’s triumph!






